The concept of “chained blocks” was initially proposed to solve the double-spending problem in Bitcoin; as a result, the term “blockchain” progressively became more generalised. Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology that links users together online to produce a trustworthy transaction record without the need for a third party. It is a database that stores records but, unlike a regular database, a blockchain secures data in a way that makes system manipulation, tampering and falsification impossible.
In blockchain technology, the data are stored in “blocks”, which are then sequentially arranged and interlinked to create an unbreakable chain. Each block in a chain comprises three basic components: data, a nonce (a 32-bit whole number), and a hash (a 256-bit number coupled to the nonce). The cryptographic hash is produced by a nonce at the beginning of a chain. Unless it is mined, the data in the block is regarded as signed and permanently bound to the nonce and hash.
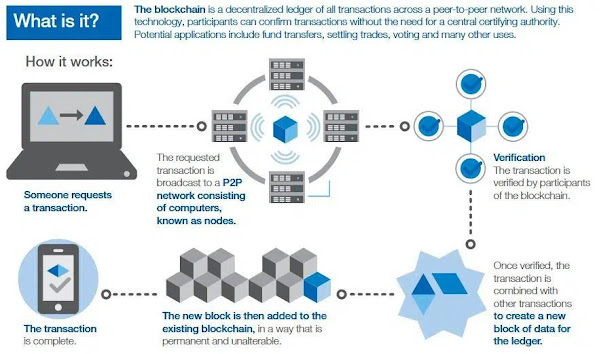
When a transaction occurs, it is registered as a “block” of data, and each block is linked to the ones preceding and following it, forming an irrevocable chain referred to as a blockchain. Each additional block reinforces the previous block’s verification, and thus the entire blockchain. This makes the blockchain tamper-evident, delivering the critical power of robustness.

No comments:
Post a Comment