A lithium-ion battery is composed of cathode, anode, separator and electrolyte. A lithium-ion battery applied at smartphones, power tools and EVs uses liquid electrolyte solution. On the other hand, a solid-state battery uses solid electrolyte, not liquid.
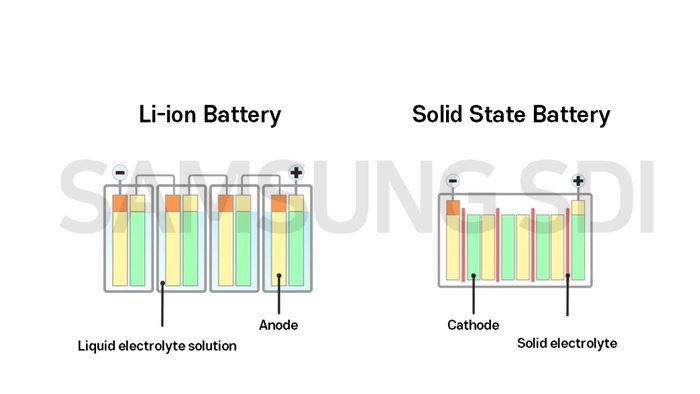
[ Structure of Li-ion battery(left) and solid-state battery(right) ]
If you look at the image above, the Li-ion battery, which is commercially used, has a separator that keeps cathode and anode apart, with liquid electrolyte solution. On the other hand, the solid-state battery uses solid electrolyte, not liquid electrolyte solution, and the solid electrolyte plays a role of a separator as well.
What users most worry about a lithium-ion battery is safety. The current Li-ion battery has a risk of battery damage such as swelling caused by temperature change or leakage caused by external force since it uses liquid electrolyte solution. Therefore, we need devices or components that can improve safety.
However, a solid-state battery with solid electrolyte shows improved stability with a solid structure, and increased safety since it maintains the form even if the electrolyte is damaged.
Reasons to develop a solid-state battery
Then, why do we need a solid-state battery? It is to increase capacity of EV batteries.
Market research companies expect that EVs will replace ICEVs(internal combustion engine vehicles), and become the mainstream in the auto industry. And to become the unarguable leader in the industry, EV should have the similar level of mileage as the current ICEV, and it is important to increase the battery capacity of an EV battery to do so.
There are two ways to increase capacity. First is increasing the number of batteries. But in this case, the battery price goes up and batteries take up so much space in the vehicle.
A solid-state battery has higher energy density than a Li-ion battery that uses liquid electrolyte solution. It doesn’t have a risk of explosion or fire, so there is no need to have components for safety, thus saving more space. Then we have more space to put more active materials which increase battery capacity in the battery.
A solid-state battery can increase energy density per unit area since only a small number of batteries are needed. For that reason, a solid-state battery is perfect to make an EV battery system of module and pack, which needs high capacity.
[A downsized solid-state battery(right) with the same capacity as the Li-ion battery(left)]
Market trend of a solid-state battery
Samsung SDI is currently working on developing the solid-state battery. We are also jointly developing the battery with other institutes such as Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology, Samsung R&D Institute Japan and others.
Samsung SDI has been presenting mid-to-long term solid-state battery technologies at the motor show or battery exhibitions since 2013. And we are currently at the element technology development phase for commercialization. We also said in the second quarter 2020 earnings conference call that "we have seen the possibility of developing a high-energy density and high-safety battery by combining tested materials technology and our new materials such as solid electrolyte."
In March, the Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology showed the research result of a solid-state battery that can be charged/discharged over 1,000 times with 800km of mileage on a single charge. The study about the technology that increases life cycle and safety, and reduces the size of a solid-state battery in half was published in the ‘Nature Energy’, a global scientific journal.
We must develop the solid-state battery to make the EV that goes farther and runs safely. There may be many obstacles ahead since we are at the early stage of development, but Samsung SDI will do our best to develop the ‘super-gap’ technology.
(Sources - https://www.samsungsdi.com/column/technology/detail/56462.html?listType=gallery)

No comments:
Post a Comment